Advantages of Boost Converter
Current flow in a boost converter when the transistor SW is switched off. It mentions Buck Boost Converters advantages or benefits and Buck Boost Converters disadvantages or drawbacks.

Some Properties Of Buck Boost And Buck Boost Converters Download Scientific Diagram
A boost converter step-up converter is a DC-to-DC power converter that steps up voltage while stepping down current from its input supply to its output load.

. Low operating duct cycle. The information given in the article is the basic concept of buck boost converters. Some of the boost converters can go up to 99 efficiency.
Buck step-down and boost step-up converters are the main staples of the DC-DC non-isolated power conversion industry. Advantages of Interleaving Converters Nov. The benefits of this approach are demonstrated by a two-phase boost converter design built around the LM5032 pulse-width modulation PWM controller.
1 2003 Power supply designers should be aware that all switchmode supplies are made up of buck or boost regulators with or without dc transformers. - The voltage gain is not dependent of the load. What is Buck Boost Converters.
It is demonstrated that the size and power losses in the choke of the TLBC are lower than. When should we choose continuous conduction mode or discontinuous when designing a boost converter. It offers lower operating duty cycle.
Follow edited Dec 5 2018 at. The biggest advantage of a boost converter is it offers very high efficiency. High output voltage low duty cycle low voltage on MOSFET low output voltage distortion even if the line frequency exists the waveform quality is also very good.
Benefits or advantages of Buck Boost Converters It performs step-up or step-down of voltage using minimum components. Advantages of interleaved boost converters for PFC. It offers high efficiency across wide input and output voltage ranges.
It gives higher output voltage. Boost converter 1. It is less expensive compare to most of the converters.
Search Save Online Today. But performance parameters like accuracy. Power Blogger Maxim Integrated.
Thus this is all about the Buck Boost Converter Circuit Working and applications. The advantages of the interleaved boost converter technique include low ripple amplitude and high frequency ripple power at the output and input waveforms due to an effective increase in switching frequency. Ad Free Shipping Available.
Ad Find discounts on Voltage boost converter. Erased the part of applications and I think the choice is covered with advantagesdisdvantages because one can clearly infer whether to use one or another if we are aware of. Answer 1 of 2.
Advantages of boost converter. They serve very different applications and purposes and hence a comparison seldom comes to mind and may seem like comparing apples to oranges. Low voltage on MOSFETs.
There are two types of topologies viz. Advantages versus traditional BC. Ad Find Deals on wfco 55 amp power converter in Car Tools on Amazon.
Advantages of Buck Boost Converter. In a buck converter under steady-state conditions the average current in the inductor I L is equal to the output current I OUT. Due to the voltage input being a square wave the inductor current is not constant but ripples between a maximum and a minimum.
The answer I am writing is not much different from the one I wrote in here Arpan Hota অরপণ হতs answer to What are the advantages and disadvantages of a buck-boost converter. Inverting and non. And Quora User have answered it quite well already.
It is basically one type of DC to DC converter which has output voltage either greater or less than the input voltage magnitude. I will mention some advantages and drawbacks of each mode. I may restate a few of his.
Thanks for the A2A. The most popular topology for PFC power-factor-corrected preregulators is the boost converter which has continuous input current that you can manipulate with average-current-mode-control techniques to force input current to track changes in line voltage. Dc-dc boost converter design for solar electric system presented by vsneha10891a0203 kswetha10891a0215 vsudarshan10891a0218 2.
Content block diagram basic boost converter switching device. So there is a chance to minimalize the size of capacitors and inductors whereas would be relatively large if conventional boost. - The input current is continuous and not pulsating.
The boost converter is very simple and requires very few components this is because they were originally designed and developed in the 1960s to power electronics on aircraft. It is a class of switched-mode power supply SMPS containing at least two semiconductors a diode and a transistor and at least one energy storage element. Multilevel boost converter topologies by allowing use of new efficient but relatively low voltage power devices at higher voltage and power levels are becoming popular solution in.
A capacitor inductor or the two in combination. The continuous switching mode of the boost converter consists of an inductor a capacitor and an input voltage source and a switching device.

Boost Converters Working Application Advantages Eeweb

Definition Of Buck Boost Converter Chegg Com

Some Properties Of Buck Boost And Buck Boost Converters Download Scientific Diagram

Advantages Of Buck Boost Converters Disadvantages Of Buck Boost Converters
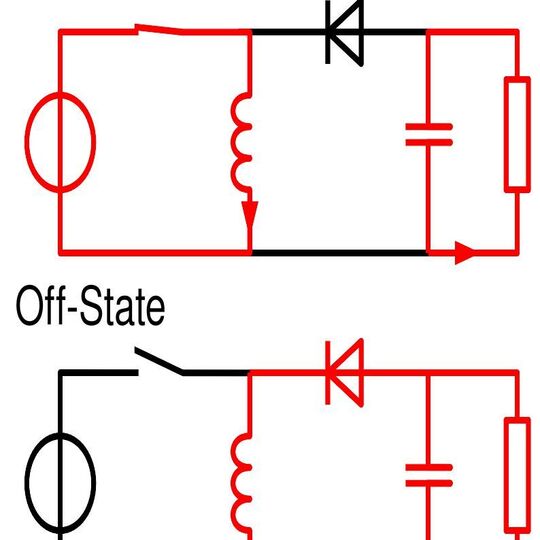
Advantages Of Buck Boost Converters

Boost Converters Working Application Advantages Eeweb
0 Response to "Advantages of Boost Converter"
Post a Comment